The life history of mankind up to the present has not been going on for only a short period of time but it actually started thousands of years ago. The condition of that time and its development up to now have shaped today’s human beings. How did people begin to communicate without writing?
The answer lies in the fact that communication is a way of interacting. Communication in pre-historic times was conducted orally and supported by the understanding of signs and pictures which were often used in communication. To let you know more about it, this chapter will discuss the development of human beings in pre-historic times.
Pre-historic is a term that refers to the time when written historical records were not available yet. It can be said that pre-historic time started at the same time as the formation of the universe, but the term is generally used to refer to the time when life started on earth. For example, dinosaurs are normally called pre-historic animals, and cavemen are usually called pre-historic men.
Since there are no written records of pre-historic time, the information about this time is obtained from various fields, such as paleontology, astronomy, biology, geology, anthropology, and archeology.
Periodization of Pre historic Time
Pre-historic time began with the first existence of human beings at the beginning of the quaternary period, i.e. in the diluvium (Pleistocene) period about 3 million years BC. The pre-historic period in Indonesia ended around the3rd to the 5th century AD when some inscriptions were found in Kutai and Tarumanegara.
The Pleistocene period was marked by the extension of ice layers on both poles of the Earth (glacial period) and intermitted by the period when the ice melted again (interglacial period). This condition happened intermittently until four times during the Pleistocene period. In tropical regions, this glacial period took the form of a rain period (pluvial period) which was intermitted by a dry period (interpluvial).
In the glacial period, the level of seawater had decreased drastically, so many seabeds ran dry and became lands. In west Indonesia, the seafloor which got dry was called Sunda Shelf, whereas, in east Indonesia, it was called Sahul Shelf.
The Sunda Shelf made Indonesian Archipelago united with continental Asia, while Sahul Shelf made the islands in east Indonesia united with Australia. That is why the flora and fauna of west Indonesia are similar to those of Asia, and on the contrary, the flora and fauna of east Indonesia are similar to those of Australia. The people who lived in the Pleistocene period were homo Erectus that supported the old stone culture (Paleolithic).
The Pleistocene period ended about 10.000 years BC, then it was followed by the coming of the alluvium period or Holocene period which continues up to now. In this period, the ancestor of today’s human beings appeared – the homo sapiens or intelligent beings.
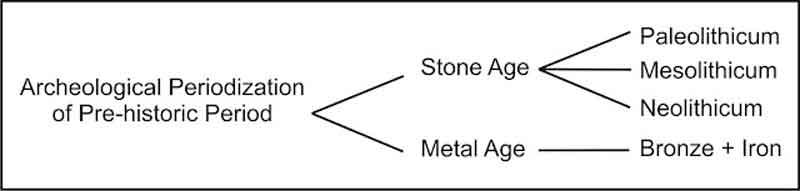
The pre-historic period can be divided according to archeological division (archeology is the science that studies the cultural products of the past in the form of objects of the cultural heritage of human beings in that period). Accordingly, the pre-historic period can be divided as follows.
Archeological Heritages
1. Stone age
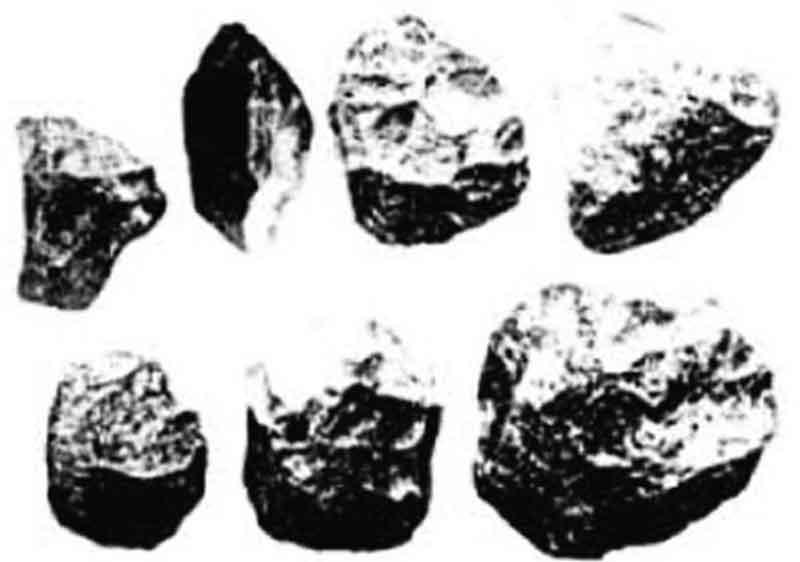

This happened before metals were known and cultural tools were mainly made of stone, in addition to wood and bone. The stone age is further divided as follows :
a. Old stone age (Paleolithic)
The old stone age is also called Paleolithic in which stone tools were still roughly made, not sharpened or polished. The life tools were also still simple in shape, for example, a hand-held ax. Based on the livelihood, this period is called the hunting and food collecting period. The supporter of this culture was homo Erectus consisting of Pithecanthropus and homo Erectus.

b. Midde stone age (Mesolithic)
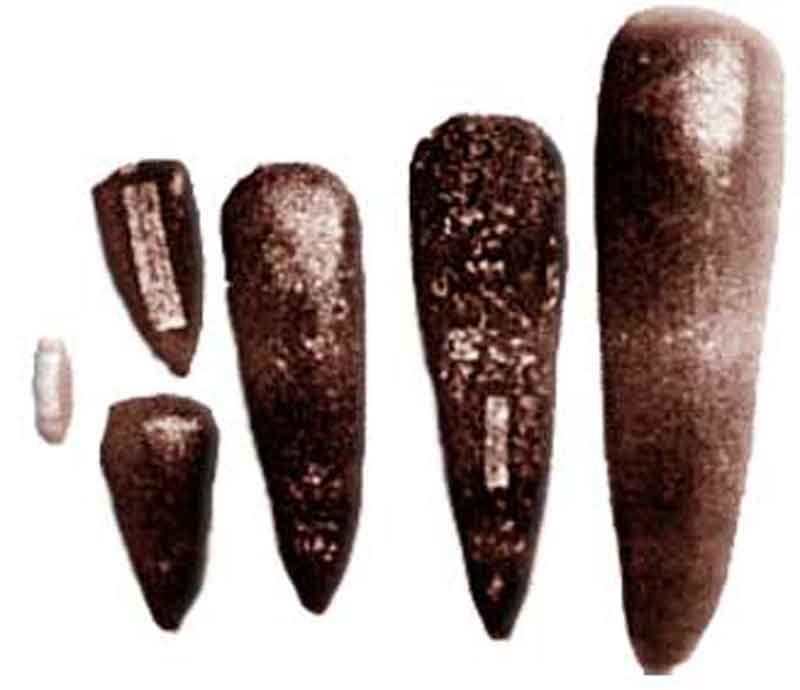

In the middle stone age (Mesolithic), some of the stone tools were already sharpened, especially the blades. People also know earthenware. This period is as know as the advanced hunting ad food-collecting period.
The supporter of this culture was o sapiens (today’s humans) consist of the Austrmelanosoid race (majority) ad Mongoloidrace (minority). This was a transitional period in which life too was more made tools of the old stone age. One example is pebble (Sumatran ax).
c. New stone age (Neolithic)
The stone tools of the new stone age (Neolithic) were already sharpened and polished, so they looked smooth and beautiful. Besides, earthenware, woven material, and batik were already known. This period is also called the cropping period.
The supporter of this culture was homo sapiens consisting of Mongoloid race (majority) and Austromelanosoid race (minority). Examples of tools of this period are the square ax and oval ax.
2. Metal age
In the metal, people were already able to make tools of metal, in addition to stone tools. People already knew the technique for smelting metal and mold it into tools they wanted. There were two methods of making metal tools, one was by using a stone mold and this technique was called bivalve, while the other way was by using a clay mold and was and this was called ‘acire perdue‘.
This period was also called the craftsmanship period because there appeared a group of people who were experts in making things by hand. The metal age is divided as follows :
a. The copper Age
People used copper as a cultural means. These cultural means were only known in some parts of the world. It was not known in Southeast Asia (including Indonesia).
b. The Bronze Age
In this time, people were already able to mix copper with other metals to obtain a harder metal. The most dominant discoveries were tools made of bronze, so this period was called the bronze age.
c. The Iron Age
In this period, people were already able to smelt iron ore and cast it to make the tools they needed. Smelting iron is more difficult than smelting copper or bronze because it needs a higher temperature, +/- 3500° C.
The metal age in Indonesia was dominated by bronze tools, so the period was also called the bronze age. There were only a few iron tools invented in this time and most of them were similar to bronze tools in shape. Most iron tools were invented in the historic time.
It should be noted, however, that although the metal age began, it does not mean the stone age had completely ended because in the metal age stone tools still developed, even now they still do. The term metal age is only used to show that in that period, people started to know and use metal tools.
The development of the metal age in Indonesia was different from Europe because the metal age in Europe passed 3 phases, they were the copper age, bronze age, and iron age. In Indonesia and also in Southeast Asia, however, there was no copper age, the area only experienced two ages – the bronze age and iron age which happened almost at the same time.
In between the stone age and the metal age, megalithic culture developed, that is a culture that used large stones as tools, and the peak of the culture even happened in the metal age. That is the description of the periodization of the pre-historic period archeologically. To better understand the description, please study the chart below :
Chart below Periodization of Prehistoric